A) forms vesicles only when large amounts of material are being transported.
B) does not require ATP.
C) is a form of exocytosis.
D) involves ingestion of liquids rather than particles.
E) does not require the formation of vesicles.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A red blood cell that is placed in a hypertonic solution
A) loses water.
B) gains water.
C) floats.
D) ruptures.
E) neither gains nor loses water.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
White blood cells digest other cells and so would be expected to
A) have mitochondria to energize them.
B) have large numbers of lysosomes.
C) possess cilia on their surfaces so they can move quickly.
D) expel their nuclei to make room for all of the cells they eat.
E) excrete excess salt as a result of all this eating.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT associated with interphase?
A) The centrioles duplicate.
B) The cell grows.
C) The cell does nothing but rest.
D) The cell does what it is designed to do.
E) The DNA replicates.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The leading strand of DNA is formed as
A) soon as the lagging strand is formed.
B) a continuous strand, adding to the 5´ end.
C) a continuous strand, adding to the 3´ end.
D) a template.
E) short segments called Okazaki fragments.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following activities is a function of the plasma membrane?
A) cell metabolism
B) transport of products from the nucleus to the endoplasmic reticulum
C) recognition of bacterial cells by the immune system
D) digestion of unneeded cell organelles
E) detoxification
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cytoplasm is found
A) in the nucleus.
B) outside the nucleus but inside the plasma membrane.
C) in the cisternae of the endoplasmic reticulum.
D) on the cristae of the mitochondria.
E) between the phospholipids in the plasma membrane.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cell with abundant peroxisomes would most likely be involved in
A) detoxification activities.
B) secretion.
C) protein synthesis.
D) storage of glycogen.
E) cellular communication.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
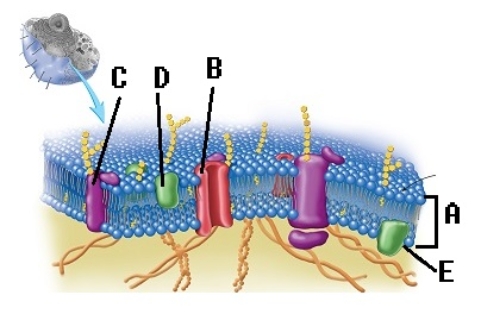 -What structure does "C" represent on the diagram of the plasma membrane?
-What structure does "C" represent on the diagram of the plasma membrane?
A) phospholipid bilayer
B) integral protein
C) membrane channel protein
D) peripheral protein
E) internal membrane surface
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following events occurs in the nucleus?
A) ATP synthesis
B) ribosomal proteins formed
C) chromatin condenses to form chromosomes
D) manufacture of phospholipids
E) None of these events occurs in the nucleus.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
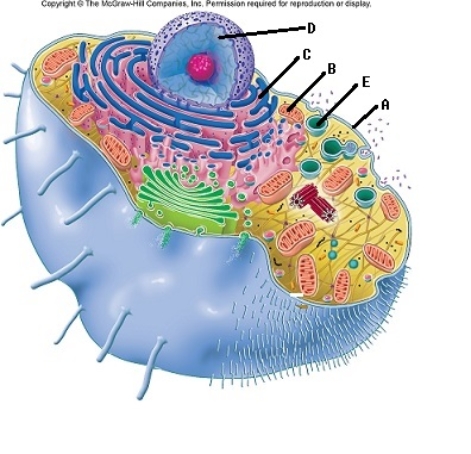 -The cell is the basic unit of life. All cellular structures exhibit special functions. Match the structure with its function. What is the function of "E"?
-The cell is the basic unit of life. All cellular structures exhibit special functions. Match the structure with its function. What is the function of "E"?
A) major site of ATP synthesis when oxygen is available
B) contains digestive enzymes
C) directs cellular activities, contains DNA
D) site of protein synthesis
E) outer boundary of cell, controls entry and exit of substances
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The collection of carbohydrates, glycolipids, and glycoproteins of the plasma membrane is called the
A) intercellular fluid.
B) phospholipid.
C) fluid mosaic.
D) glycocalyx.
E) extracellular membrane.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of cell would have an abundance of lysosomes?
A) liver cells that detoxify hydrogen peroxide
B) fibroblast (makes protein fibers)
C) white blood cell, a phagocyte
D) cardiac muscle cells (require large amounts of ATP)
E) mucus cell (secretes mucus)
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of membrane proteins can catalyze chemical reactions on the inner or outer surfaces of the plasma membrane?
A) channel protein
B) carrier proteins
C) receptor proteins
D) enzymes
E) marker molecules
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
A) moves materials out of the cell.
B) is a type of passive transport.
C) exhibits specificity.
D) does not need ATP; the receptors supply the energy.
E) occurs if oxygen is available.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT an example of a cytoplasmic inclusion?
A) lipid droplets
B) hemoglobin
C) actin filaments
D) melanin
E) lipochrome
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nucleoli
A) are located in the cytoplasm.
B) are important for the formation of the Golgi apparatus.
C) have a distinct membrane.
D) regulate movement of materials into the nucleus.
E) produce ribosomal subunits.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following cell organelles is CORRECTLY matched with its function?
A) ribosome - energy production
B) microtubules - cell support
C) mitochondria - protein synthesis
D) smooth ER - ATP production
E) nucleolus - contains the genetic material of the cell
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT consistent with active transport?
A) uses cell energy
B) movement is against a concentration gradient
C) movement is with a concentration gradient
D) exhibits competition and saturation
E) involves a carrier
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cell that breaks down and recycles proteins would have large numbers of
A) peroxisomes.
B) secretory vesicles.
C) proteosomes.
D) lysosomes.
E) rough ER.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 227
Related Exams