A) 1 → 2 → 3 → 4 → 5
B) 2 → 3 → 5 → 4 → 1
C) 3 → 2 → 5 → 1 → 4
D) 4 → 3 → 1 → 2 → 5
E) 5 → 1 → 2 → 4 → 3
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The "selectivity" of a particular ion channel refers to its
A) permitting passage by positive but not negative ions.
B) permitting passage by negative but not positive ions.
C) ability to change its size depending on the ion needing transport.
D) binding with only one type of neurotransmitter.
E) permitting passage only to a specific ion.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following questions, refer to the graph of an action potential in Figure 37.1.
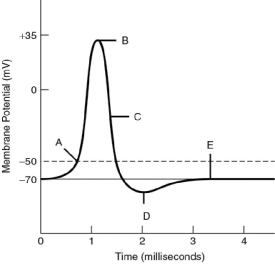 Figure 37.1
-The cell is not hyperpolarized; however, repolarization is in progress, as the sodium channels are closing or closed, and many potassium channels have opened, at label
Figure 37.1
-The cell is not hyperpolarized; however, repolarization is in progress, as the sodium channels are closing or closed, and many potassium channels have opened, at label
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
E) E.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Action potentials move along axons
A) more slowly in axons of large diameter as compared to those of small diameter.
B) by the direct action of acetylcholine on the axonal membrane.
C) by activating the sodium-potassium "pump" at each point along the axonal membrane.
D) more rapidly in myelinated than in nonmyelinated axons.
E) by reversing the concentration gradients for sodium and potassium ions.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A toxin that binds specifically to voltage-gated sodium channels in axons would be expected to
A) prevent the hyperpolarization phase of the action potential.
B) prevent the depolarization phase of the action potential.
C) prevent graded potentials.
D) increase the release of neurotransmitter molecules.
E) have most of its effects on the dendritic region of a neuron.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Neural transmission across a mammalian synapse is accomplished by
A) the movement of sodium and potassium ions from the presynaptic neuron into the postsynaptic neuron.
B) impulses traveling as electrical currents across the synapse.
C) impulses causing the release of a chemical signal and its diffusion across the synapse.
D) impulses ricocheting back and forth across the synapse.
E) the movement of calcium ions from the presynaptic into the postsynaptic neuron.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Functionally, which cellular location is the neuron's "decision-making site" as to whether or not an action potential will be initiated?
A) axonal membranes
B) axon hillocks
C) dendritic membranes
D) mitochondrial membranes
E) presynaptic membranes
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The membrane potential that exactly offsets an ion's concentration gradient is called the
A) graded potential.
B) threshold potential.
C) equilibrium potential.
D) action potential.
E) inhibitory postsynaptic potential.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A neuropeptide that might function as a natural analgesic is
A) acetylcholine.
B) epinephrine.
C) endorphin.
D) nitric oxide.
E) GABA.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Motor neurons alter skeletal muscle activities by releasing neurotransmitter because
A) they are electrically coupled by gap junctions to the muscles.
B) their signals bind to receptor proteins on the muscles.
C) their signals reach the muscles via the blood.
D) their light pulses activate contraction in the muscles.
E) they are connected to the internal neural network of the muscles.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The activity of acetylcholine in a synapse is terminated by its
A) active transport across the presynaptic membrane.
B) diffusion across the presynaptic membrane.
C) active transport across the postsynaptic membrane.
D) diffusion across the postsynaptic membrane.
E) degradation by a hydrolytic enzyme on the postsynaptic membrane.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why are action potentials usually conducted in one direction?
A) The nodes of Ranvier conduct potentials in one direction.
B) The brief refractory period prevents reopening of voltage gated Na+ channels.
C) The axon hillock has a higher membrane potential than the terminals of the axon.
D) Ions can flow along the axon in only one direction.
E) Voltage-gated channels for both Na+ and K+ open in only one direction.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a direct result of depolarizing the presynaptic membrane of an axon terminal?
A) Voltage-gated calcium channels in the membrane open.
B) Synaptic vesicles fuse with the membrane.
C) The postsynaptic cell produces an action potential.
D) Ligand-gated channels open, allowing neurotransmitters to enter the synaptic cleft.
E) An EPSP or IPSP is generated in the postsynaptic cell.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Immediately after an action potential passes along an axon, it is not possible to generate a second action potential; thus, we state that the membrane is briefly
A) hyperexcitable.
B) refractory.
C) fully depolarized.
D) above threshold.
E) at the equilibrium potential.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that excessive consumption of ethanol increases the influx of negative chloride ions into "commonsense" neurons whose action potentials are needed for you to act appropriately and not harm yourself or others. Thus, any resulting poor decisions associated with ethanol ingestion are likely due to
A) increased membrane depolarization of "commonsense" neurons.
B) increased membrane hyperpolarization of "commonsense" neurons.
C) more action potentials in your "commonsense" neurons.
D) more EPSPs in your "commonsense" neurons.
E) fewer IPSPs in your "commonsense" neurons.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An example of ligand-gated ion channels is
A) the spreading of action potentials in the heart.
B) acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction.
C) cAMP-dependent protein kinases.
D) action potentials on the axon.
E) graded hyperpolarization.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following questions, refer to the graph of an action potential in Figure 37.1.
 Figure 37.1
-The period in which voltage-gated potassium channels are open and hyperpolarization has yet to occur is at label
Figure 37.1
-The period in which voltage-gated potassium channels are open and hyperpolarization has yet to occur is at label
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
E) E.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A graded hyperpolarization of a membrane can be induced by
A) increasing its membrane's permeability to Na+.
B) decreasing its membrane's permeability to H+.
C) decreasing its membrane's permeability to Cl-.
D) increasing its membrane's permeability to Ca++.
E) increasing its membrane's permeability to K+.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ionotropic receptors are found at synapses operated via
A) ligand-gated ion channels.
B) second-messenger-gated ion channels.
C) electrical synapses.
D) inhibitory, but not excitatory, synapses.
E) excitatory, but not inhibitory, synapses.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Saltatory conduction is a term applied to
A) conduction of impulses across electrical synapses.
B) an action potential that skips the axon hillock in moving from the dendritic region to the axon terminal.
C) the rapid movement of an action potential reverberating back and forth along a neuron.
D) jumping from one neuron to an adjacent neuron.
E) jumping from one node of Ranvier to the next in a myelinated neuron.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 68
Related Exams